Trans-post pyramidal fissure approach for cerebellar vermis tumors
If the brain tumor is deep, it is necessary to cut into a part of the brain.
The brain has wrinkles called sulci, so if you peel off these wrinkles as carefully as possible, you can reach deep into the wrinkles without cutting the brain.
For all brain tumors, I try to use these wrinkles to perform minimally invasive surgery.
There is a fist-sized brain called the cerebellum at the back of the head, and there is an important brain called the cerebellar vermis that balances the body vertically in the middle. In order to remove the hemangioma, we opened the posterior pyramidal fissure, a groove located behind the vermis, and completely removed the hemangioma without causing any symptoms. I named the trans-post pyramidal fissure approach and wrote an English paper with a diagram of the approach.
Neurologia Medico-Chirurgica 51:371-375, 2011
full textpostpydamidal fissure approach
Figures A,B,C
Schematic demonstration of the postpyramidal fissure approach. The midline sagittal sections of the brainstem (Figure A) and cerebellum (Figure B) show the direction of the postpyramidal fissure approach. The relationship (Figure C) between the postpyramidal fissure approach and the fastigial nucleus, the emboliformic nucleus, and the dentate nucleus (midline sagittal section and coronal section through the dentate nucleus of the cerebellum). There are no critical structures between the bottom of the postpyramidal fissure and the nearest part of the floor of the fourth ventricle.
Figure A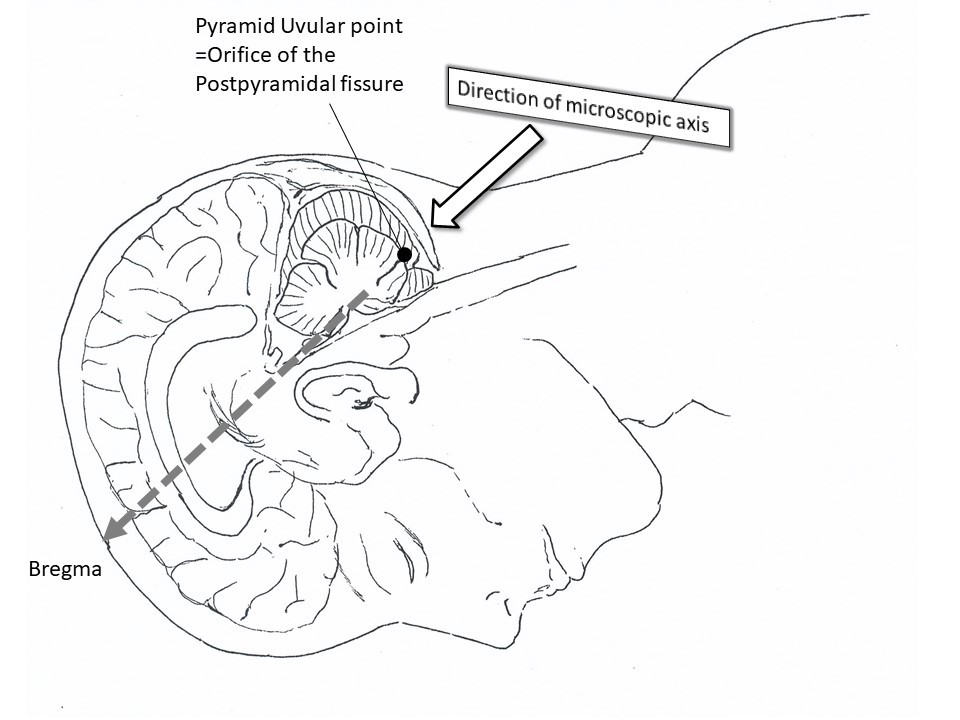
Figure B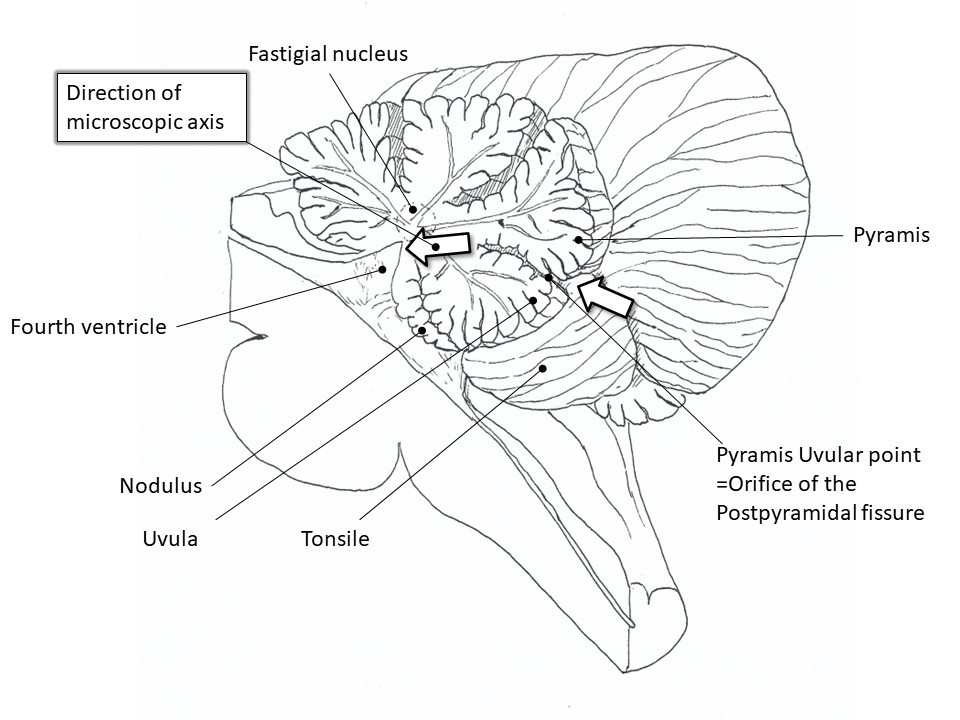
Figure C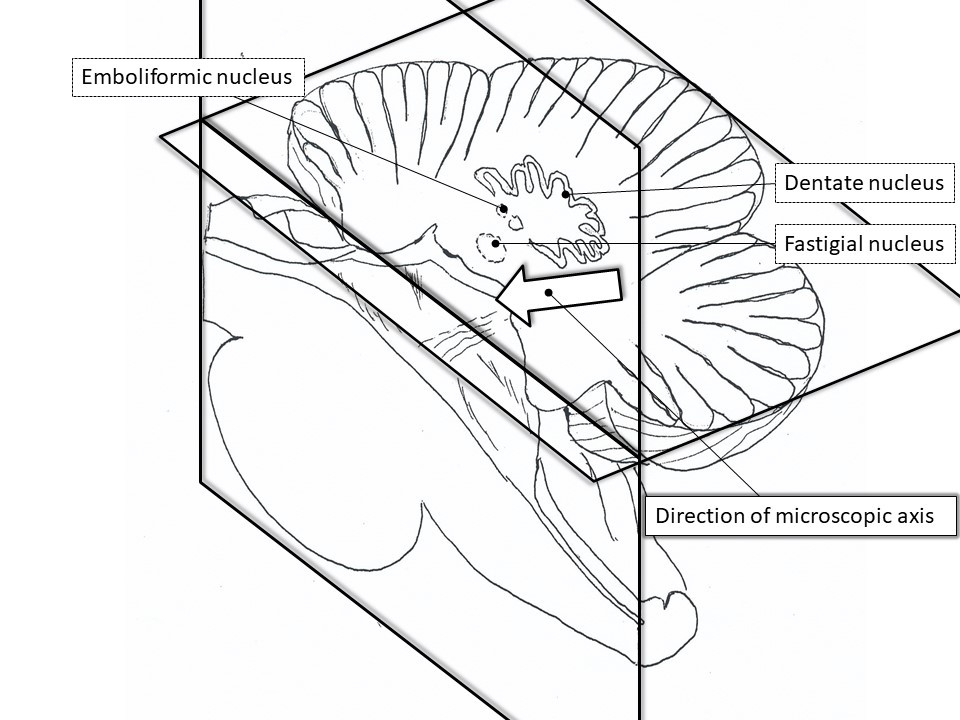
This is an example of my surgery, but in all brain tumor removal surgeries, I try to be conscious of the brain sulcus and try not to cut into the brain as much as possible, and I also instruct the staff to do so.
Next, the important points for accurately grasping how far the brain tumor has been removed during the brain tumor removal surgery and whether the brain and nerve functions are preserved are:
⇒ Please see "Knowing Brain Tumor Treatment Part 2 Intraoperative Navigation and Intraoperative Monitoring".
An important point for predicting postoperative recurrence by pathological examination is
⇒ See also "Knowing the treatment of brain tumors Part 4 Pathology of postoperative recurrence of brain tumors".

Snowboading head injury
coffee intake prevent silent cerebral infarction
Stroke:general information
treatment of intracerebral hemorrhage
treatment of subarachoid hemorrhage
carotid endoarterectomy
STA-MCA anastomosis
Moyamoya disease
arterio-venous malformation: AVM
MRI T2* WI
Tumor removal part 1 : FLAIR
Tumor removal part 2: navigation and monitoring
Tumor removal part 3 : approach through sulci
Tumor removal part 4 : MIB-1 labeling index



 HOME
HOME HOME JAPANESE
HOME JAPANESE Self Introduction
Self Introduction Paper/Presentation
Paper/Presentation